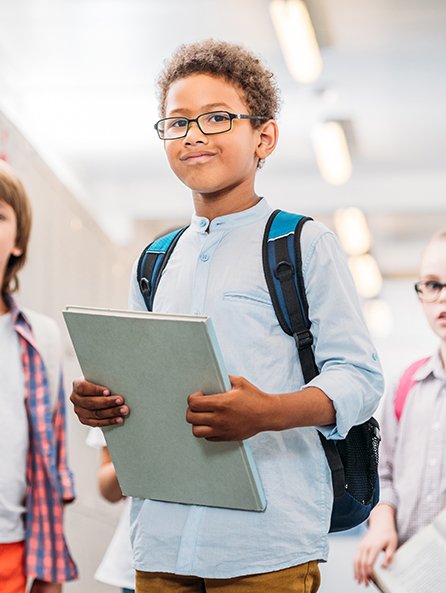
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, the urgency to adapt to virtual learning environments has never been more pressing. The shift from traditional classrooms to online platforms has created a dynamic and challenging landscape for educators, students, and educational diagnosticians alike. The need to effectively organize virtual learning projects and peer activities is paramount to ensure that learning continues seamlessly and that students remain engaged and supported. This guide delves into the critical steps necessary to organize virtual learning initiatives that are not only effective but also engaging and responsive to the needs of all participants.
Understanding the Role of Educational Diagnosticians in Virtual Learning
Educational diagnosticians play a pivotal role in the virtual learning ecosystem. Their expertise in assessing and identifying students’ learning needs is crucial in tailoring educational experiences that are both effective and inclusive. In virtual settings, the absence of physical cues necessitates a more nuanced approach to assessment and support. Educational diagnosticians must leverage digital tools and platforms to conduct assessments, analyze data, and collaborate with educators to develop individualized learning plans. Their involvement ensures that all students, especially those with special educational needs, receive the appropriate support to thrive in virtual learning environments.
Planning and Structuring Virtual Learning Projects
The foundation of any successful virtual learning project lies in meticulous planning and structured organization. Begin by clearly defining the project’s objectives, outcomes, and timelines. Utilize project management tools to create detailed plans that outline each phase of the project, assign responsibilities, and set deadlines. This structured approach not only ensures that all tasks are completed on time but also provides a clear roadmap for all participants to follow. Regular check-ins and updates are essential to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments, keeping the project on track and aligned with its goals.
Designing Engaging and Interactive Peer Activities
Peer activities are a cornerstone of collaborative learning, fostering communication, teamwork, and critical thinking. In virtual settings, designing engaging and interactive peer activities requires creativity and the effective use of technology. Incorporate tools such as breakout rooms, collaborative documents, and interactive polls to facilitate dynamic interactions among students. Activities should be designed to encourage active participation, problem-solving, and peer feedback. By creating opportunities for students to collaborate and learn from each other, educators can enhance the learning experience and build a sense of community within the virtual classroom.
Utilizing Technology to Enhance Learning Experiences
Technology serves as the backbone of virtual learning, providing the platforms and tools necessary to deliver content, facilitate communication, and assess student performance. Selecting the right technological tools is crucial to the success of virtual learning projects. Consider factors such as user-friendliness, accessibility, and compatibility with existing systems when choosing platforms for video conferencing, content delivery, and assessment. Additionally, ensure that students have access to the necessary devices and internet connectivity to participate fully in virtual learning activities. Providing training and support for both educators and students on the effective use of technology can further enhance the learning experience.
Implementing Effective Communication Strategies
Clear and consistent communication is vital in virtual learning environments. Establishing effective communication strategies helps to bridge the gap created by physical distance and ensures that all participants are informed and engaged. Utilize a combination of synchronous and asynchronous communication methods, such as live sessions, discussion boards, and email updates, to reach all students. Set expectations for response times and availability to maintain a consistent flow of information. Encourage open lines of communication where students feel comfortable seeking help and providing feedback, fostering an environment of trust and collaboration.
Monitoring and Assessing Student Progress
Continuous monitoring and assessment of student progress are essential to ensure that learning objectives are being met and to identify areas where students may require additional support. Implement formative assessments, such as quizzes, surveys, and reflective journals, to gather data on student understanding and engagement. Educational diagnosticians can analyze this data to identify patterns and trends, providing insights into individual and group performance. Regular feedback should be provided to students, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement, and offering guidance on how to enhance their learning experience.
Providing Support and Resources for Students
Supporting students in virtual learning environments extends beyond academic instruction. Addressing the social and emotional well-being of students is equally important to ensure a holistic learning experience. Provide resources and support services, such as counseling, tutoring, and technical assistance, to help students navigate the challenges of virtual learning. Create opportunities for students to connect with peers and mentors, building a supportive community that fosters a sense of belonging. By addressing the diverse needs of students, educators can create an inclusive and nurturing virtual learning environment.
Evaluating and Reflecting on the Learning Experience
After the completion of virtual learning projects and peer activities, it is crucial to evaluate and reflect on the experience to identify successes and areas for improvement. Gather feedback from students, educators, and educational diagnosticians to assess the effectiveness of the project and the impact on student learning. Analyze data on student performance, engagement, and satisfaction to inform future planning and decision-making. Reflecting on the learning experience allows for continuous improvement and the development of best practices that can be applied to future virtual learning initiatives.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Virtual Learning
The transition to virtual learning presents both challenges and opportunities. By understanding the critical role of educational diagnosticians, planning and structuring virtual learning projects effectively, designing engaging peer activities, utilizing technology, implementing communication strategies, monitoring student progress, providing support, and evaluating the learning experience, educators can create virtual learning environments that are effective, inclusive, and engaging. Embracing these strategies will not only enhance the learning experience for students but also prepare them for success in an increasingly digital world.